
Metaphase II–Anaphase II: Mitosis occurs in the two new cells, dividing the chromatids into new nuclei. Prophase II: The spindle begins to form in each cell.
#Prophase 1 mitosis full
They group at opposite ends of the cell, where new nuclei form.Ĭytokinesis: The cell divides in half, creating two cells, each with one full set of chromosomes. Metaphase I, Anaphase I, and Telophase I: The homologous pairs line up at the equator, and are separated by the spindle. If you are not familiar with homologous pairs and crossing over, skip the rest of this description and go straight to the video at the end.

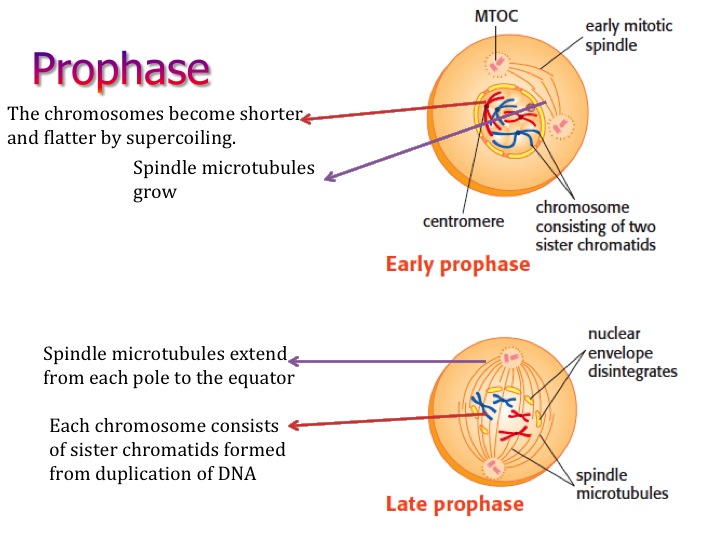
Homologous pairs (each linked to their own copy) exchange DNA through crossing over. Prophase I: Each chromosome is copied and condenses to form linked chromatids. Gametes are special because they only have one-half of the chromosomes of a normal cell. In meiosis, one cell with one full set of DNA becomes four gametes. Meiosis is a special type of cell division that creates gametes (sex cells). Click the “Take this course now” button to get started. If you’re having trouble visualizing each step of mitosis or you want some extra practice, create a free account and try our mitosis simulation for a more in-depth and complete understanding. Telophase: A new nuclear envelope forms around the DNA at each end, creating two new nuclei.Ĭytokinesis: The cell splits in the middle to form two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. The mitotic spindle latches to the centromere of each chromatid pair.Īnaphase: The spindle pulls the chromatids and their copies in opposing directions, breaking the link and gathering one complete set of chromosomes at each end of the cell. Metaphase: The chromatids line up at the equator of the cell. The nuclear envelope breaks down, and the mitotic spindle begins to form. A centromere links each chromatid to its copy, making the linked pairs look like X’s. Prophase: The chromosomes condense into chromatids. Interphase: The parent cell makes a copy of every chromosome in the nucleus, creating two full sets of DNA. The process starts with one cell and one set of chromosomes and ends with two cells and two sets of chromosomes.
Otherwise, read on to start the review! What is mitosis? The simulations will give you a clear and detailed understanding of both processes in an engaging format. If you are learning for the first time, skip the written study guide and go straight to our mitosis and meiosis simulations.
#Prophase 1 mitosis how to
It will also teach you how to study through suggested review exercises. This complete review guide will give you a crash course in mitosis and meiosis stages, and highlight the key differences between mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis and meiosis are two of the most commonly misunderstood topics on the AP Biology exam.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
